

Most people think moles are garden pests because they live in gardens, grasslands, sand dunes and other areas with soil that allows them to dig and build intricate tunnels. These creatures hunt and live underground but you will know you have a mole infestation once you notice the damage caused by their digging habits as they destroy gardens and lawns. Moles are insectivores that are often confused with voles and mice. However, you can identify them by their large front feet which have large, sharp claws and paddle-shaped hands.
What do moles eat? Moles eat insects and small invertebrates that include grubs, centipedes, snails, spiders, millipedes, and earthworms which is their favorite meal. In this article, we will answer all your questions about their physical characteristics, ravenous appetite, diet and habitat. Besides that, we will explain the damage moles cause when they invade your backyard and also look at some common myths about mole diet.
One of the most effective ways to get rid of these subterranean pests is with the best mole traps. Additionally, knowing what food moles eat and how they eat it can help you choose the right product. Moles’ dietary habits are influenced by their high appetite, odd-looking physical features and their behavioral patterns.
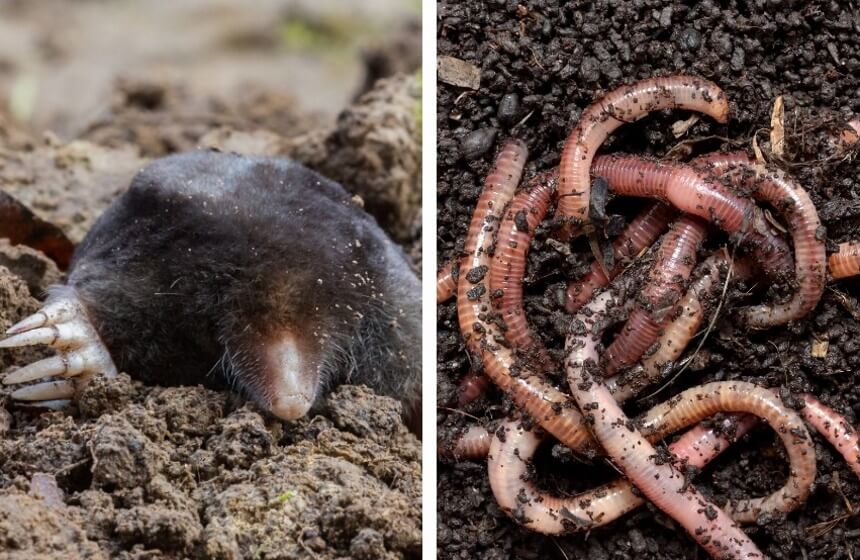

Do moles eat vegetables? Moles are carnivores, and contrary to popular belief, they do not consume roots, grass or plants. The damage is caused by the series of tunnels they create as they burrow and forage for food.
Moles like to eat earthworms, and the daily consumption of earthworms is 1.7 ounces for a mole that weighs 2.8 ounces. Depending on the mole species, some large moles will eat small mice on an occasional basis.
It is important to learn the physical characteristics of moles to understand what moles eat underground.
Moles are rotund insectivores with soft fur that is dark gray or soft brown in color. The fur moves easily in all directions to reduce resistance as moles change directions. It also makes it easy for moles to shake off dirt from the fur. Apart from giving moles greater agility to move quickly through tunnels, the velvety texture of the fur and its slick movement has made mole fur a commodity in high demand by traders.
Moles are typically around 4.4 to 6.25 inches in length, from snout to rump. Their short stout tail is 1 to 1.6 inches long. The North American species is larger in size. It is 1.25 inches tall and 7 inches long. Moles generally weigh 2.5 to 4.5 ounces in weight.
Their head features pointed snouts that are hairless and cylindrical in shape.
The snout works in a way similar to an elephant’s trunk; the shape and size of the snout allows a mole to hold steadily to an earthworm while eating it. The snout protrudes about an inch in front of a mole’s face.
Moles have no visible ears, but they have small eyes that almost seem nonexistent and fairly useless because they only detect light and darkness.
Considering their bizarre features, what do moles eat in the wild? The structure of their feet is one of the features that help them to hunt for insects and small invertebrates underground. Moles have small rear appendages and wide front feet that look like flaps stuck to the sides of the body. The large and muscular front feet have large claws and the paddle shape of their feet allows moles to dig and almost swim as they move underground. Moles have six digits because of the extra thumb on their front feet which allows them to move soil.
Moles also have a strong sense of smell that enables them to detect food and follow scents left by other moles to mark their tunnels. In addition to that, moles have a strong sense of feel that they use to detect air movements and identify holes in their tunnels that lead outside. Once moles identify a hole in a tunnel that they often use, they actively plug it.
Mole breeding season is between February and May. The male ventures into foreign territory in search of a female partner and two males will fight if they find themselves competing for the same territory. The male produces a high pitched squeal to indicate it is available for mating. 3 to 5 baby moles are born at a time in March or April since the gestation period of a mole is approximately seven weeks. Coastal moles tend to have larger litters than inland moles and they also mate much later in March through April.
Young moles leave the nest after 30 to 45 days to find their own territories since they can tunnel and fend for themselves by about three weeks.
Moles use scent to mark and differentiate between territories. They become aggressive when moles from a different territory come to their burrow. However, it is more likely for female territories to overlap and female moles have smaller territories than male territories.
Moles are mammals that are subterranean in nature. So, how exactly do moles eat and live underground? According to The Telegraph Trusted Source Secret of how moles breathe underground revealed The secret of how moles are able to breathe underground has been discovered. www.telegraph.co.uk , scientist found that a biochemical adaptation enables moles to tolerate high levels of carbon dioxide and to inhale their own exhaled air. Can you imagine burrowing underground where there significantly low oxygen levels and doing it as you breathe into a paper bag? No wonder moles fascinate us despite the havoc they wreak in our gardens.
Moles consume earthworms, larvae and other small invertebrates they can find in the earth.
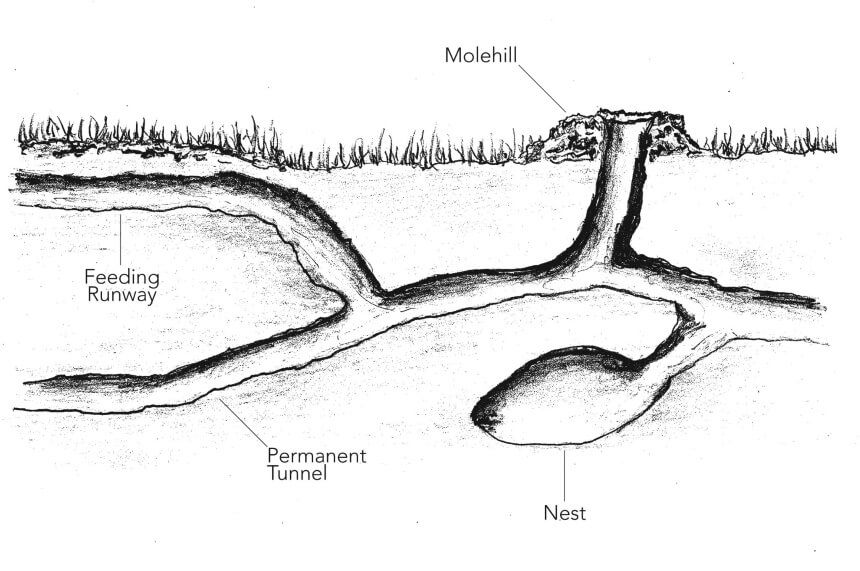
Moles make tunnels that they use for different purposes. They use some tunnels to sleep or give birth and use deeper tunnels as living spaces and storage spaces.
Moles also build feeding tunnels that include special traps for earthworms. Once the mole detects that an earthworm has found its way into the tunnel, it will locate and bite the worm. The saliva has a toxin that paralyzes the prey. The mole can then store the paralyzed earthworm for later consumption. You can drastically reduce and eliminate a mole infestation with poisonous baits or gassers or traps from the best mole killers that will prevent them from destroying your yard or garden.
Do moles eat dirt? A mole uses its front feet to squeeze out dirt from the worm’s guts before eating it. The design of the snout accounts for a mole’s dietary patterns since the snout enables a mole to feed with minimal effort and resistance from the prey.
What do moles eat in the winter? It might surprise you to learn that moles do not hibernate. After all, they live underground where they are already used to cold temperatures. Instead of hibernating when the upper ground layers freeze, moles move deeper underground to follow food source such as insects in warmer areas.
Mating season begins in late winter. In late winter, the mole mating season begins and males search out females who then give birth in early spring, which explains the increase in mole activity in the spring.
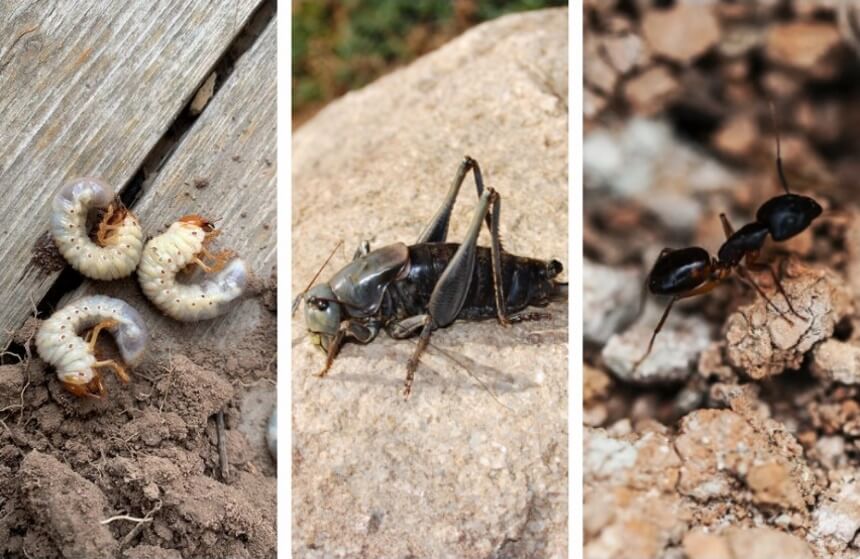

What do moles eat in Florida? According to the University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences Trusted Source Moles in Lawns - UF/IFAS Extension University of Florida, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences Extension outreach is a partnership between state, federal, and county governments to provide scientific knowledge and expertise to the public. The University of Florida (UF), together with Florida A&M University (FAMU), administers the Florida Cooperative Extension Service. sfyl.ifas.ufl.edu , garden moles eat beetle larvae, crickets and ants. Considering most of us view moles as pests, it is ironic that moles actually reduce pest population by eating insects that can harm plants. Moles also aerate soil by pushing the loose soil they dig up to the surface. Ground moles eat invertebrates such as grubs, millipedes, centipedes, slugs and snails they come across in the soil.
Earthworms are the best meal for a mole and their high appetite means a mole can eat several earthworms, around 200, in a day. There are multiple earthworms in the soil which ensures that moles have constant food supply. Earthworms also have high water content in their bodies and eating worms allows moles to hydrate.
Do moles like to eat vegetables? No, they don’t. As insectivores, they prefer invertebrates such as snails and slugs and insects like spiders, beetles, ants, millipedes and centipedes. They also eat grubs and insect larvae.
What do baby moles eat? Baby moles, known as pups, only drink their mother’s milk for 4 to 5 weeks. After that, they are weaned and they start eating insects and earthworms.

You would be surprised at what food moles eat in the garden. Contrary to what many people believe, ground moles do not eat vegetables, plants or roots. They come to your garden to search for insects, larvae, worms and other invertebrates. However, they are constantly creating tunnels and excavating loose soil which consequently disrupts the roots of grass and plants and causes them to eventually die. Moles are often mistaken for voles because voles travel in the tunnels made by moles. Voles are the one known to feed on potatoes and roots.
As mentioned above, the food that moles eat in the garden or underground does not include plants and vegetables, but insects, larvae and invertebrates. The damage you see in your yard comes from their burrowing activity which weakens roots and causes the attached plants, shrubs and trees to die. You can avoid this problem with the biodegradable Mole Scram Professional which uses a strong odor that is offensive to moles to drive them away.

Dish soap is said to kill mole crickets although what it does is to draw them out in the same way it can draw out the earthworms that are a staple food for moles, therefore forcing the moles to starve or search elsewhere for food. You would have the most success with the best mole repellents that are also safe to use around children and pets.
Another popular myth is that you can use gum and marshmallows to kill moles. If you search “how to get rid of moles in yard with Juicy fruit gum” on the internet, you will see several results. However, killing moles with marshmallows would not work. If you look at the main marshmallow ingredients such as sugar, egg whites and corn syrup, none of them would appeal to moles, knowing what we know about what food moles eat and their hunting habits. Neither would gum, unless the mole ingests it accidentally and even then, there is still no proof that it would kill a mole.
Ground moles and garden moles eat the same food i.e. larvae, insects and invertebrates in the soil. Moles do not eat dirt or vegetables. The dying plants are as a result of weakened roots cause by moles as they burrow and create tunnels in search of food. The mole diet correlates with their physical characteristics, ravenous appetite that uses food as fuel for their constant digging, and their behavior when it comes to breeding, hunting and social life. What do moles eat in the winter? The same food they eat during other seasons. The only difference is that they have to dig deeper into the ground in the winter to find insects that have moved to warmer areas. You can eliminate moles from your yard with repellents, traps and other types of mole killers available at an affordable cost.